Top 5 SEO Mistakes You Make on Your Business Website: How to Fix Them
- Kethshan Ind
- SEO Basics
- 12 Mins Read
Table of Contents
Introduction
For small and medium business owners, creating an online presence that drives traffic and converts visitors into customers can be a challenging goal. Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is one of the most effective ways to boost visibility and reach more potential clients, yet many business websites fall short because of common SEO mistakes. These errors can hurt your rankings, lead to higher bounce rates, and even reduce your revenue.
In this article, we’ll walk through the top 5 SEO mistakes that could be negatively impacting your business website, from slow site speed and duplicate content to keyword stuffing and poor internal linking. By addressing these issues, you’ll create a smoother, faster, and more user-friendly experience that both search engines and visitors will love.
Let’s dive into the most common SEO mistakes and learn how to fix them effectively, starting with one that can directly impact your bottom line—site speed performance.
Mistake 1: Neglecting Site Speed Performance
In today’s fast-paced digital world, speed is everything. Site speed—the time it takes for your website to load—is a crucial factor not only for user experience but also for SEO rankings and revenue.
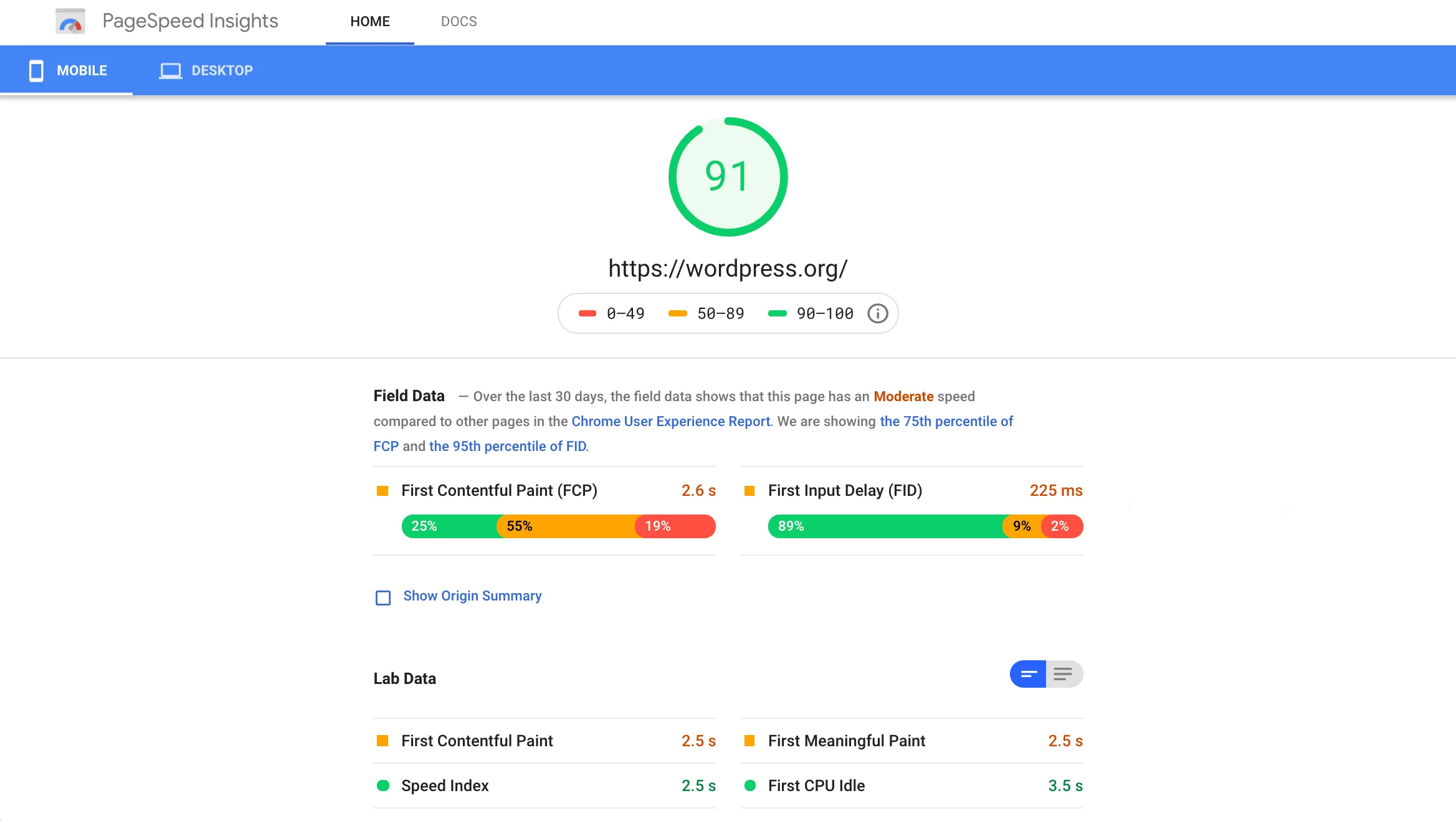
Research shows that 83% of users expect a website to load in under three seconds, while 40% will abandon a site that takes any longer. This means if your website is slow, you risk losing almost half of your potential visitors before they even see your content.
Google considers site speed one of its top ranking factors, making it a key component of SEO. A slow site not only frustrates users but also signals to Google that your website may not provide a high-quality experience. Over time, this can lower your search engine rankings, decrease your visibility, and reduce traffic—ultimately impacting your bottom line.
Why Site Speed Matters for Your Business:
- User Retention – Faster websites engage users more effectively, encouraging them to browse longer and reducing bounce rates.
- Higher Conversions – A smooth, fast-loading experience keeps potential customers on your site, increasing the likelihood of conversions, be it sales, sign-ups, or inquiries.
- Improved SEO Rankings – Google prioritizes sites that load quickly, rewarding them with higher rankings and increased visibility on SERPs (Search Engine Results Pages).
If you’re not prioritizing site speed, you’re not just missing out on better rankings—you’re also losing out on potential revenue.
How to Fix Site Speed Performance:
1. Optimize All Images
Images are often the largest files on a website and can drastically slow down load times if they’re not optimized. Compress images using tools like TinyPNG or ImageOptim without compromising quality. Choose efficient formats like WebP or JPEG over heavier formats like PNG for photographs.
2. Implement Browser Caching
Caching saves elements of your site, such as images, CSS, and JavaScript files, in a visitor’s browser, so they don’t need to be reloaded every time the user returns. Use a caching plugin (e.g., WP Rocket or W3 Total Cache for WordPress) to reduce load times for repeat visitors and improve overall speed.
3. Minify JavaScript, CSS, and HTML Files
Minification removes unnecessary characters (like spaces and comments) from your site’s code, making it lighter and faster to load. Tools like UglifyJS for JavaScript or online resources such as Minifier can help reduce file sizes and improve performance.
4. Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN)
A CDN, like Cloudflare or Akamai, distributes your content across a network of servers worldwide, so users access data from the server closest to their location. This reduces load times, particularly for users who are geographically far from your main server.
5. Reduce HTTP Requests
Every file or element on a page, including images, scripts, and stylesheets, makes a separate HTTP request, which can slow down load time. Simplify your design by limiting the number of elements on each page and using CSS sprites (single images that combine multiple icons) for frequently used icons and graphics.
6. Evaluate Your Hosting Provider
Low-cost hosting plans may seem budget-friendly but can often result in slower performance, especially if you’re on a shared hosting plan with limited resources. If your site is still slow after implementing these fixes, consider upgrading to a faster, more reliable hosting provider or switching to a dedicated or VPS hosting plan for improved performance.
7. Enable Lazy Loading for Images
Lazy loading allows images below the fold (those not visible on the screen immediately) to load only when the user scrolls down to view them. This reduces initial load times and improves the first impression for users by prioritizing the visible content.
8. Monitor and Test Regularly
Regularly test your site speed using tools like Google PageSpeed Insights and GTmetrix. These tools provide a detailed breakdown of performance issues, along with specific recommendations for improvement. Monitoring your site’s performance helps you stay ahead of issues before they affect user experience or SEO.
Mistake 2: Duplicate Content Issues
Duplicate content occurs when identical or highly similar content appears on multiple pages within a single website or across different websites. This can happen for various reasons, from accidentally creating multiple versions of the same page to republishing content from external sources. While duplicate content might seem harmless, it can severely impact SEO and user experience.
When search engines encounter duplicate content, they struggle to determine which version is the most relevant to show in search results. This confusion can result in “keyword cannibalization,” where different pages compete for the same search terms, diluting their effectiveness.
Additionally, search engines prioritize unique, valuable content for users, so duplicate pages may be seen as low-quality or redundant, which can lead to lower rankings and less visibility.

Why Duplicate Content Makes Problems for Your Business:
- Lower Rankings: Google and other search engines aim to provide diverse results for users. When they detect duplicate content, they may rank only one version or avoid ranking any of the pages altogether.
- Diluted Authority: When multiple pages cover the same topic with similar content, they compete for search engine authority, which can lower each page’s individual impact.
- Reduced User Trust: Users want fresh, unique content. Repetitive or duplicate content across different pages can make a website appear unprofessional or spammy, which can hurt user trust and lead to higher bounce rates.
How Duplicate Content Issues Commonly Arise:
- Multiple Pages with Similar Information: For instance, separate pages created for similar products or services without enough unique content on each page.
- URL Variations: Different versions of a URL for the same content (such as with or without “www” or trailing slashes) can lead to unintentional duplicate pages.
- Scraped or Copied Content: Republishing content from other sites or relying too heavily on manufacturer descriptions without adding original insights.
How to Fix Duplicate Content Issues:
1. Run a Site Audit for Duplicate Content
Use SEO tools like Semrush or Ahrefs to conduct a site audit and identify pages with duplicate content. These tools can flag any pages that closely resemble one another, helping you locate duplication issues efficiently.
2. Monitor Indexed Pages in Google Search Console (GSC)
Google Search Console can provide insights into which pages are indexed and alert you to potential duplicate content issues. Check the “Coverage” and “Enhancements” reports to see if Google has flagged any duplicate content or indexing issues.
3. Use Canonical Tags to Consolidate Similar Content
Canonical tags are a powerful solution for managing duplicate content. A canonical tag tells search engines which page is the “master” version of similar content, so they know which one to prioritize in search results. For example, if you have multiple pages targeting similar keywords, set one page as canonical to signal it as the main version.
4. Merge or Consolidate Redundant Pages
If you have several pages with overlapping content that don’t serve a unique purpose, consider combining them into a single, comprehensive page. Consolidating duplicate pages reduces competition for the same keywords, strengthens the page’s SEO value, and improves user experience by providing more cohesive information.
5. Create Unique Content for Each Page
Ensure that each page on your website serves a distinct purpose and provides unique value. This can involve writing original descriptions, adding insights or tips relevant to the topic, and focusing on specific keywords. Even if the topic is similar, differentiating the content with additional details and examples can enhance its value.
6. Check URL Variations and Redirect Appropriately
Duplicate content often arises due to multiple URLs leading to the same content (e.g., with “www” vs. without, or with parameters). Implement 301 redirects to consolidate these variations into a single, preferred URL. This helps search engines understand the structure of your site and avoids dividing traffic among duplicate URLs.
7. Avoid Copying Content from External Sources
While it’s tempting to republish content from other sites, this can result in “scraped content,” which harms SEO. Search engines prioritize original content, so focus on creating content that adds unique insights and stands out from the competition. If you must reference external sources, rewrite the content in your own words and include original perspectives.
8. Add Value with User-Generated Content
One way to enrich similar pages is by incorporating user-generated content, such as testimonials, FAQs, or case studies. Adding this type of unique content to your pages not only differentiates them but also makes them more valuable to users and search engines.
9. Review Product or Service Pages for Uniqueness
If you’re an e-commerce or service-based business, product and service pages can easily become repetitive. Instead of using identical descriptions, try to create distinct descriptions or add specific details about each product or service’s unique benefits, features, or applications. Highlighting specific use cases or adding customer reviews can make these pages more distinct.
Mistake 3: Keyword Stuffing
Keyword stuffing is an outdated SEO tactic where keywords are used excessively in an attempt to manipulate rankings. This often leads to unnatural, repetitive, and low-quality content that provides little value to readers. While keywords remain essential for helping search engines understand your content, overusing them can do more harm than good.
Keyword stuffing can make your content appear spammy, reducing its readability and user engagement. Search engines like Google have become more sophisticated in detecting this tactic, and they penalize websites that rely on it. Not only can this lower your rankings, but it can also erode trust with visitors who are put off by the unnatural flow of keyword-heavy content.
Signs of Keyword Stuffing:
- Repetitive Phrases – Overusing the same phrase in every sentence or paragraph.
- Unnatural Language – Content that doesn’t read smoothly because it’s packed with keywords instead of natural language.
- Irrelevant Keywords – Adding keywords that don’t fit with the topic just to capture extra traffic.
Why Keyword Stuffing Hurts Your Business:
- Reduced User Engagement – Content that feels forced or robotic tends to drive readers away, leading to higher bounce rates and less time on site.
- Lower Search Rankings – Google’s algorithms actively penalize pages that use keyword stuffing, which can drop your page’s rankings or remove it from search results entirely.
- Loss of Brand Credibility – Poor-quality content affects your brand’s reputation, making it seem like you’re more focused on “hacks” than on delivering value to your audience.
How to Fix Keyword Stuffing:
1. Use Keywords Sparingly and Strategically
Aim to use your primary keyword in key locations—such as the title, meta description, first paragraph, and a few times throughout the content. Instead of repeating the same keyword excessively, use it naturally and in context. For example, if your primary keyword is “SEO for small businesses,” you could use variations like “SEO strategies for small business owners” or “small business SEO tips.”
2. Include Secondary and Related Keywords
Secondary or related keywords, often called “LSI (Latent Semantic Indexing) keywords,” provide context and help search engines understand the topic better without overloading your content. Tools like Ahrefs, Semrush, or Google’s “related searches” feature can help you find relevant terms to incorporate naturally.
3. Prioritize Content Quality and Readability
High-quality content is engaging, informative, and valuable to readers. Focus on providing helpful insights, answering questions, and offering clear explanations rather than simply trying to rank for specific keywords. Use tools like the Hemingway Editor or Grammarly to ensure your writing is readable and flows smoothly.
4. Follow On-Page SEO Best Practices
Apply on-page SEO principles to optimize your content without stuffing. These include:
o Using Descriptive, Engaging Titles and Meta Descriptions: Titles and descriptions should be clear, concise, and contain the main keyword without overdoing it.
o Optimize Headers (H1, H2, H3 Tags): Use headers to break up content and include keywords sparingly in subheadings. This improves readability and allows search engines to understand the page structure better.
o Utilize Alt Text for Images: Add keywords to image alt text naturally. Alt text should describe the image while including relevant terms, but avoid forcing keywords.
5. Use Descriptive Anchor Text for Internal Links
When linking internally, use descriptive and relevant anchor text that feels natural. Instead of using the same keyword repeatedly as anchor text, vary the phrases and ensure they make sense within the content. For example, instead of always using “SEO tips,” you might alternate with “learn about SEO strategies” or “boost your site’s visibility with SEO.”
6. Check Content Readability
Aim for a readability score of 80% or higher to ensure your content is accessible and easy to understand. Readability tools, like Yoast SEO for WordPress or the Readability Test Tool, help ensure that sentences and paragraphs are clear and concise, avoiding the repetitive language that often accompanies keyword stuffing.
7. Focus on Creating Valuable, In-Depth Content
Instead of trying to rank by packing a page with keywords, develop in-depth content that provides comprehensive information on the topic. Long-form, informative content ranks well because it fully addresses user intent, increasing the likelihood of users spending more time on your page. When your content meets the audience’s needs, they’re more likely to stay, interact, and share, boosting your site’s SEO naturally.
8. Review and Edit Regularly
After writing your content, review it to ensure keywords are used naturally. Editing tools like Grammarly or a simple manual review can help you spot sections that feel overstuffed or repetitive. Focus on readability and flow, adjusting any areas that seem awkward or forced.
9. Update Content Based on Performance Data
Use Google Analytics and Google Search Console to monitor the performance of your content over time. Look at metrics like bounce rate, time on page, and engagement to gauge whether users are responding well. If a page isn’t performing as expected, revisit the content to make adjustments, focusing on readability, user engagement, and natural keyword integration.
Mistake 4: Ignoring User Experience (UX)
User Experience (UX) encompasses all aspects of how users interact with your website. Good UX design makes it easy for visitors to navigate, find information, and complete actions. When UX is ignored, users may find the website frustrating or confusing, leading to higher bounce rates, lower engagement, and missed conversions.
Google has made UX a priority, incorporating Core Web Vitals into its ranking algorithm to reward sites that offer a fast, smooth, and responsive experience. A poor UX can result in lower SEO rankings and decreased visibility on search engines, as well as damage to your brand’s reputation. Today, users expect intuitive navigation, quick load times, and a seamless experience across devices. If your website doesn’t meet these standards, users may not stay long enough to engage with your content or convert.

Common UX Pitfalls:
- Poor Navigation – Users struggle to find the information they need because the site structure is confusing or links are hard to find.
- Outdated Design – An old or cluttered design can make the site look unprofessional, deterring visitors.
- Lack of Mobile Optimization – With most searches happening on mobile, a site that isn’t mobile-friendly can alienate a large segment of users.
- Slow Loading Pages – Pages that take too long to load discourage users and lead to high bounce rates.
How UX Affects Your Business:
- Improves Conversions – A user-friendly site that guides visitors to complete actions (e.g., sign-ups, purchases) can significantly increase conversions.
- Reduces Bounce Rates – When users find your website easy to navigate and engaging, they are more likely to stay longer and explore multiple pages.
- Enhances SEO – Google rewards sites with a positive UX by ranking them higher, as these sites are more likely to satisfy user intent.
How to Fix User Experience (UX):
1. Optimize Site Navigation and Layout
- A clear and intuitive navigation structure helps users find information quickly, improving both UX and SEO.
- Use Descriptive Menu Labels: Label menu items clearly to help users understand where each link will take them.
- Include a Search Bar: A search function helps users quickly locate specific content, which is particularly useful on content-rich websites.
- Organize Content Logically: Group similar content under related categories. For example, if you have a blog, separate posts by topic or theme for easy browsing.
2. Make Your Website Mobile-First
- Google now primarily indexes mobile versions of sites, meaning a poor mobile experience can harm your rankings. Optimizing for mobile ensures that your site is accessible and user-friendly on all devices.
- Use Responsive Design: Ensure that your site automatically adjusts its layout, images, and content based on the screen size.
- Optimize Touch Elements: Make buttons, links, and form fields easy to tap, with adequate spacing to prevent misclicks.
- Reduce Clutter: Simplify your mobile layout to improve load speed and readability. Avoid large blocks of text and opt for concise, scannable content.
3. Conduct Regular A/B Testing
- A/B testing allows you to compare two versions of a page to see which performs better in terms of user engagement and conversions. Testing various elements, such as CTA button colors, placement, and copy, can provide valuable insights.
- Test Different Design Elements: Experiment with elements like button colors, headlines, and form placements to find combinations that enhance engagement.
- Measure Engagement Metrics: Use data like click-through rates, time on page, and conversion rates to assess which version of a page resonates better with users.
- Implement Changes Based on Results: Use the winning design changes to optimize other areas of your site, gradually improving overall UX.
4. Review Core Web Vitals for Speed and Stability
- Google’s Core Web Vitals focus on loading performance, interactivity, and visual stability—key metrics that impact UX.
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Measures loading speed. Aim to load main content within 2.5 seconds.
- First Input Delay (FID): Measures interactivity. Ensure elements like buttons and links respond quickly to clicks.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Measures visual stability. Avoid elements that shift or cause layout changes as the page loads.
Use Google PageSpeed Insights and Lighthouse to analyze these metrics and implement recommended improvements.
5. Leverage Data to Understand User Behavior
- Data-driven insights can reveal how users interact with your site and highlight areas for improvement.
- Use Google Analytics: Track metrics such as bounce rate, time on page, and session duration to identify pages with poor engagement. High bounce rates may signal UX issues on specific pages.
- Analyze Heatmaps: Tools like Hotjar provide visual data on where users click, scroll, and exit, helping you pinpoint navigation or layout issues.
- Run User Experience Surveys: Gather feedback from users through on-site surveys. Ask questions about their experience, ease of navigation, and any frustrations they encounter.
6. Enhance Content Layout and Readability
- Well-organized content keeps users engaged, helping them understand and interact with your message effectively.
- Use Short Paragraphs and Headings: Break content into short, readable sections, using headings to guide users through the page.
- Add Visual Elements: Include images, videos, or infographics to make the content more engaging and easier to understand.
- Apply Consistent Branding and Design: Consistency in colors, fonts, and design elements helps users navigate your site with ease and builds brand recognition.
7. Optimize for Accessibility
- Accessibility ensures that all users, including those with disabilities, can navigate and interact with your website effectively. Accessibility is also a ranking factor and reflects positively on your brand.
- Use Alt Text for Images: Alt text helps screen readers interpret images, making your site accessible to visually impaired users.
- Provide Keyboard Navigation Options: Ensure users can navigate using only a keyboard, as some users may not be able to use a mouse.
- Maintain Color Contrast: Use high-contrast colors for text and backgrounds to ensure readability for visually impaired users.
Mistake 5: Weak Internal Linking and External Linking Architecture
Linking architecture—the structure of internal and external links on your website—is fundamental to SEO and user experience. A robust linking structure helps search engines crawl your website, understand the relationships between pages, and assess the relevance of your content. When internal and external linking is neglected or done poorly, it can hinder your site’s discoverability, reduce page authority, and confuse users navigating your site.
A well-thought-out linking strategy supports both user navigation and SEO, creating a network of connections that guide users through your content and send strong signals to search engines about which pages are most valuable. Weak internal linking can make it difficult for users to find relevant information on your site, and weak external linking limits your site’s reach and credibility in your industry.
Why Linking Architecture Matters for Your Business:
- Boosts Page Authority: Effective internal linking distributes “link juice” or authority across pages, boosting the SEO value of key pages.
- Improves Site Navigation: Internal links help users explore more content, leading to longer sessions and lower bounce rates.
- Enhances SEO: Search engines prioritize sites that are easy to crawl. Strong linking makes it easier for search engines to index your pages, which can lead to higher rankings.
- Builds Industry Credibility: External links to reputable sources demonstrate your commitment to providing accurate, reliable information, building trust with both search engines and visitors.
Common Issues in Weak Linking Architecture:
- Broken Links: Links that lead to non-existent pages result in poor user experience and wasted SEO potential.
- Orphan Pages: Pages with no incoming links are harder for users and search engines to find, diminishing their visibility.
- Overwhelming or Sparse Linking: Too few links limit discoverability, while too many can appear spammy and reduce the impact of each link.
- Non-Descriptive Anchor Text: Anchor text that doesn’t indicate what the linked page is about can confuse users and diminish SEO value.
How to Fix Weak Internal Linking and External Linking:
1. Find and Fix Broken Links
Broken links not only frustrate users but also disrupt the flow of authority throughout your website. Conduct regular checks to identify and repair broken links.
- Use SEO Tools: Tools like Screaming Frog, Ahrefs, or Google Search Console can help you locate broken links across your website.
- Redirect or Remove: If a linked page no longer exists, set up a 301 redirect to guide users to a relevant page. If the broken link isn’t essential, consider removing it altogether.
- Regular Maintenance: Check for broken links at least quarterly to keep your site in good shape and prevent users from encountering 404 errors.
2. Strengthen Internal Linking for Important Pages
A strategic internal linking structure guides users to valuable content and helps search engines understand your site hierarchy.
- Identify Key Pages: Pinpoint important pages (e.g., product pages, service pages, cornerstone content) and ensure they are linked from various relevant locations within your site.
- Add Internal Links in High-Traffic Pages: Linking to important pages from high-traffic content, such as blog posts, can help pass authority and increase visibility for those key pages.
- Use Natural Anchor Text: Anchor text should be descriptive, reflecting the content of the linked page without keyword stuffing. For example, instead of “click here,” use “learn more about SEO best practices.”
3. Locate and Link Orphan Pages
Orphan pages are pages on your site that have no internal links pointing to them, making it hard for search engines to discover them.
- Identify Orphan Pages: Use tools like Screaming Frog to find pages without inbound links.
- Integrate Orphans into Your Site Structure: Add links to orphan pages from relevant content sections or your main navigation. For example, if you have an orphaned blog post on “SEO for Beginners,” link it within other beginner-friendly guides.
- Organize with Content Clusters: Group similar pages around a main topic, creating a “hub-and-spoke” or content cluster model that strengthens the relevance of each page within a specific theme.
4. Optimize XML Sitemap for Efficient Crawling
An XML sitemap is a roadmap for search engines, helping them crawl and index your site more effectively. If your sitemap is outdated or poorly organized, search engines may miss important pages.
- Include Only Relevant Pages: Ensure that only important, canonical pages are listed in your sitemap. Avoid including “thin” content or duplicate pages.
- Update Regularly: Make sure your sitemap reflects the current state of your website. Whenever you add, delete, or significantly update pages, regenerate your sitemap and submit it to Google Search Console.
5. Practice Smart External Linking
Linking to authoritative, trustworthy external sites can enhance your content’s credibility and add value to your users. However, external linking should be done thoughtfully.
- Link to Reputable Sources: Only link to well-regarded sources that provide genuine value to your readers. Avoid linking to low-quality or irrelevant sites, as this can harm your credibility.
- Open External Links in New Tabs: This practice keeps users on your site while allowing them to explore additional resources without navigating away.
- Use External Links Sparingly: Too many external links can dilute your content’s focus. Aim to include only a few highly relevant external links per page, enhancing credibility without overwhelming users.
6. Create a Logical Link Structure with Content Hierarchies
Content hierarchies, or content clusters, provide users and search engines with a clear path through your site’s content. Organizing your site this way improves navigation and SEO value.
- Implement Topic Clusters: Arrange related pages around a “pillar” page that covers a broad topic. Each cluster page links back to the pillar page and vice versa, creating a strong, organized structure.
- Build Internal Links Across Clusters: Cross-link between related clusters when relevant, helping users explore related content and supporting search engines in understanding connections between topics.
7. Use Descriptive Anchor Text to Enhance Link Relevance
Anchor text is a powerful way to communicate link relevance to both users and search engines.
- Avoid Generic Phrases: Instead of using vague phrases like “read more” or “click here,” use anchor text that describes the linked page, such as “SEO basics for small businesses.”
- Limit Exact-Match Keywords: Overusing exact-match keywords in anchor text can appear manipulative to search engines. Use variations and natural language to keep anchor text diverse and helpful.
8. Audit and Adjust Your Linking Strategy Regularly
SEO and user behavior evolve, so it’s essential to revisit and refine your linking strategy periodically.
- Analyze Engagement Metrics: Use tools like Google Analytics to track user behavior on pages with updated internal and external links. Metrics like session duration and bounce rate can indicate how well users are engaging.
- Update Outdated Links: Check for broken external links and update them with more recent, authoritative resources. Outdated links reduce content value and can erode trust.
Need Assistance with Your SEO Strategy?

Kethshan Induruwage
Kethshan has been providing digital marketing solutions for over 10 years. Kethshan has been a SEO specialist, SEM, SMM, content manager and coordinator, and strategist. His expertise lies in bridging the gap between branding, growth & performance marketing, tech marketing, and analytics. He is passionate about constructing and executing innovative strategies that amplify brand awareness and drive conversions.